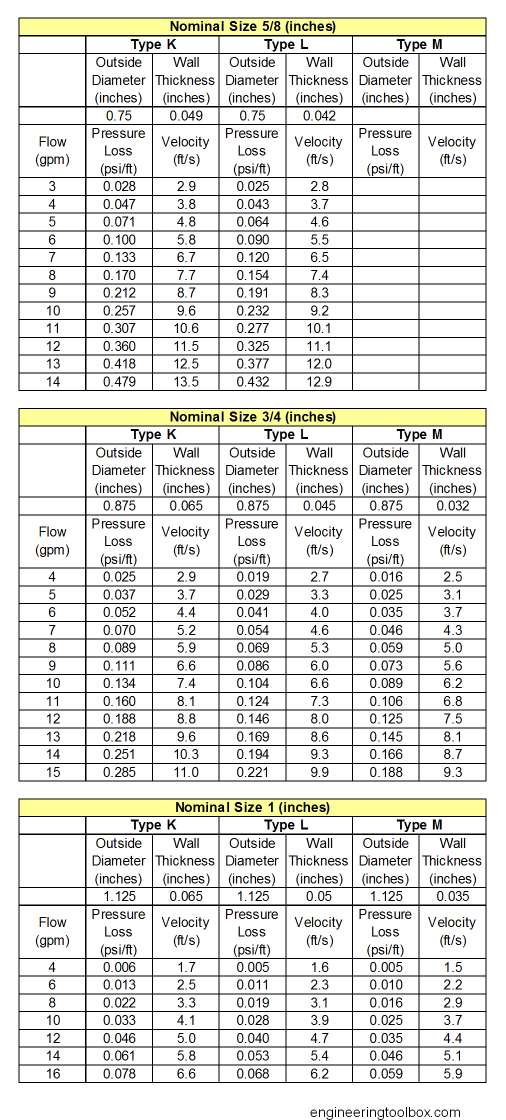
- Absolute Roughness Of Copper Pipe
- Absolute Roughness Of Copper Nickel Pipe
- Equivalent Roughness Of Copper Pipe
Material: Nature of Material: Roughness mm Roughness inch Steel pipe: drawn, new: 0.02 - 0.1: 0.0008 - 0.004: welded, new: 0.05 - 0.1: 0.002 - 0.004. 1.3 Relative Roughness Factors for various New Clean Pipes 6 1.4 Head Loss through Conduits—Hazen and Williams Equation 7 1.5 Typical Roughness Coefficients 8 TABLE A Steel—Commercial 9 B Steel—Large Fabricated 15 C Steel—Galvanised27 D Ductile Cast Iron—Uncoated 35 E Ductile Cast Iron—Cement Lined 43 F Copper Tube 51. The relative roughness of a pipe is its roughness divided by its internal diameter or e/D, and this value is used in the calculation of the pipe friction factor, which is then used in the Darcy-Weisbach equation to calculate the friction loss in a pipe for a flowing fluid. Note: Absolute roughness of copper pipe? Apparatus: Pipe apparatus. A copy of these notes and observation sheet. Procedure – Pressure drop (Heal Loss) in pipes: Measure the temperature of the water and use published data to determine the viscosity of the water. (Table 1) Table 1: Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity in SI. Relative roughness - the ratio between absolute roughness an pipe or duct diameter - is important when calculating pressure loss in ducts or pipes with the Colebrook Equation. Relative roughness can be expressed as r = k / dh (1).

 For each pipe material either a single pipe roughness value or a range of roughness values is normally provided by the manufacturer. The roughness value, usually denoted as e
For each pipe material either a single pipe roughness value or a range of roughness values is normally provided by the manufacturer. The roughness value, usually denoted as eAbsolute Roughness Of Copper Pipe
, is used in the calculating the relative roughness of a pipe against the size of its diameter.Absolute Roughness
The roughness of a pipe is normally specified in either mm or inches and common values range from 0.0015 mm for PVC pipes through to 3.0 mm for rough concrete pipes.

Absolute Roughness Of Copper Nickel Pipe
Relative Roughness
The relative roughness of a pipe is its roughness divided by its internal diameter or e/D, and this value is used in the calculation of the pipe friction factor, which is then used in the Darcy-Weisbach equation to calculate the friction loss in a pipe for a flowing fluid.
Pipe Materials and Common Pipe Roughness Values
| Material | e (mm) | e (inches) |
| Concrete | 0.3 - 3.0 | 0.012 - 0.12 |
| Cast Iron | 0.26 | 0.010 |
| Galvanized Iron | 0.15 | 0.006 |
| Asphalted Cast Iron | 0.12 | 0.0048 |
| Commercial or Welded Steel | 0.045 | 0.0018 |
| PVC, Glass, Other Drawn Tubing | 0.0015 | 0.00006 |
Pipe Materials and Pipe Diameter Database
Equivalent Roughness Of Copper Pipe
Our Pipe Flow Expert software comes with its own database of pipe materials and pipe diameters, which includes the pipe roughness values and standard material schedules of many types of pipe. Users can also add their own pipe data for any material and any pipe size if required.
Pipe materials in the Pipe Flow Expert pipe database include Cast Iron (Class A,B and C), Copper Tube (Type X,Y,K,L,M), HDPE (SDR 7.3 to SDR 26), PVC (Schedule 40, 80, and CL100 to CL315), Stainless Steel (Schedule 5s, 10s, 40s), Steel (Schedule 40,80,160) and more.
You can download Pipe Flow Expert for a free trial and see how it makes it easy to draw, design and calculate the flows and pressure drops in your pipe system.